
Ī limitation of the α-factor secretion signal is that the signal sequence portion directs posttranslational translocation across the ER membrane. Several of those attempts focused on modifying the α-factor secretion signal. pastoris, but the level of secretion varies widely, prompting efforts to improve secretion efficiency.
This bipartite secretion signal has proven to be effective for secreting multiple heterologous proteins in P.
#Snapgene viewer asterisk pro
The α-factor signal sequence is removed by a signal peptidase in the ER lumen, and the pro region is cleaved by the Kex2 processing protease in the Golgi. This secretion signal consists of two parts: a 19-amino acid N-terminal signal sequence that directs translocation into the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), followed by a 66-amino acid pro region that mediates receptor-dependent packaging into ER-derived COPII transport vesicles (Additional file 1: Figure S1). pastoris, the most common secretion signal is that of the S. pastoris is designated a Generally Recognized As Safe (GRAS) organism, and its similarity to Saccharomyces cerevisiae enables the sharing of protocols and of certain genetic elements such as secretion signals.įor heterologous protein production in P. pastoris secretes only low levels of endogenous proteins, a property that facilitates downstream processing because the heterologous protein comprises the vast majority of the protein in the medium. pastoris, including its capacity to grow in both defined and complex media, the possibility to reach high cell densities of up to 130 g/L of dry cell weight, and availability of the strong and tightly regulatable AOX1 (alcohol oxidase 1) promoter, which can be induced with methanol or repressed with glucose or glycerol. This popularity stems from several advantages of P. In recent decades, the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris ( Komagataella sp.) has become one of the most popular platforms for heterologous protein production. These benefits are likely to be most evident for proteins that can fold in the cytosol and for oligomeric proteins. The improved secretion signal confers dramatic benefits for the secretion of certain proteins from P. Similar findings were obtained with the lipase BTL2, which exhibited 10-fold enhanced secretion with the improved secretion signal. The resulting improved secretion signal enhanced secretion of E2-Crimson up to 20-fold compared to the levels obtained with the original α-factor secretion signal. Moreover, an allelic variant of the α-factor pro region reduced aggregation of the E2-Crimson construct in the ER. When paired with the α-factor pro region, the Ost1 signal sequence yielded much more efficient secretion than the α-factor signal sequence. Secretion and intracellular localization were assessed using as a model protein the tetrameric red fluorescent protein E2-Crimson. cerevisiae Ost1 signal sequence, which promotes cotranslational translocation into the ER, followed by the α-factor pro region.
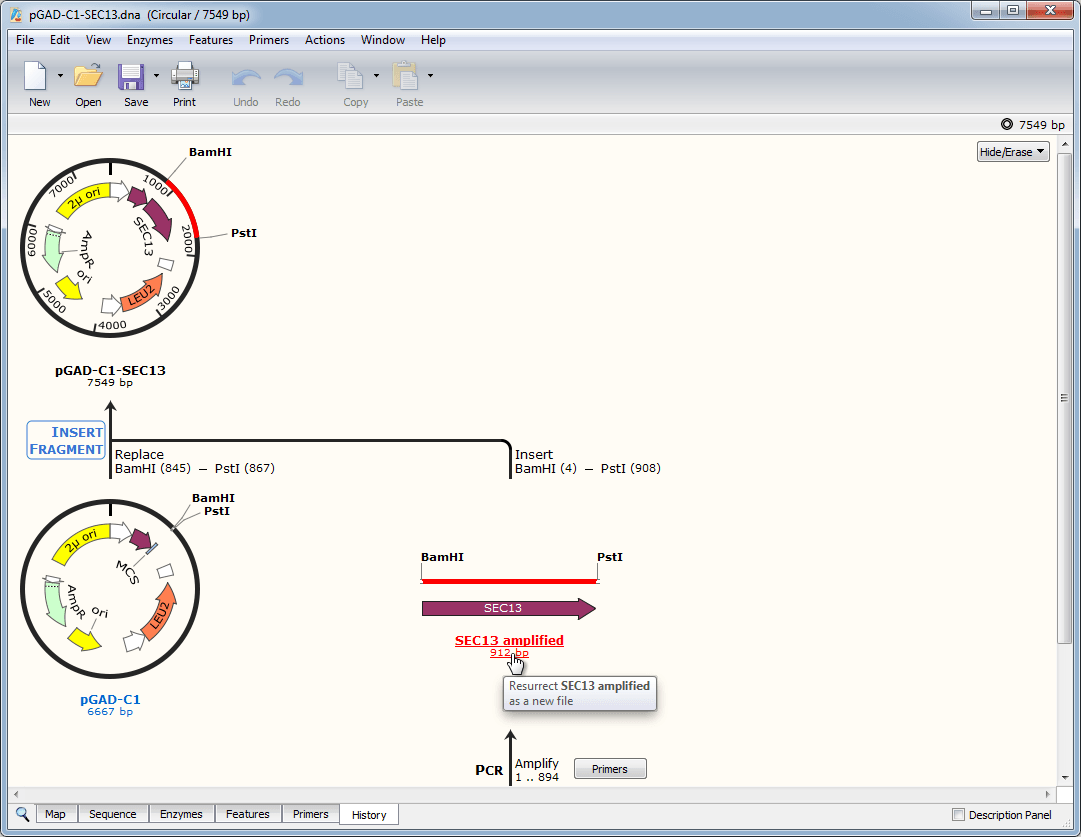
We engineered a hybrid secretion signal consisting of the S. This study addresses both limitations of the pre-pro-α-factor secretion signal. In addition, if a protein self-associates, the α-factor pro region can potentially cause aggregation, thereby hampering export from the ER. However, this secretion signal promotes posttranslational translocation into the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), so proteins that can fold in the cytosol may be inefficiently translocated and thus poorly secreted. For this yeast, the most commonly used secretion signal is the N-terminal portion of pre-pro-α-factor from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The budding yeast Pichia pastoris ( Komagataella sp.) is widely employed to secrete proteins of academic and industrial interest. Proteins can be secreted from a host organism with the aid of N-terminal secretion signals.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
